What Is the Normal Range for Blood Sugar?
Normal blood sugar v. high blood sugar
By the age of 35, it is advised that everyone be checked for type 2 diabetes and prediabetes using a blood glucose test. People who have symptoms or risk factors for diabetes, have a family history of the disease, or come from a certain ethnic background might need to get evaluated sooner. Following a blood test in which the patient fasted for the whole night, normal blood sugar would be 99 mg/dL or below. An unhealthy blood sugar level is 100 mg/dL or above. Prediabetes is defined as blood sugar levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL, and type 2 diabetes is defined as blood sugar levels of 126 mg/dL or above. For a diagnosis to be made, at least two abnormal blood sugar test results are required.
Another useful metric for diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes is hemoglobin A1C,
which measures blood glucose levels over a three-month period.
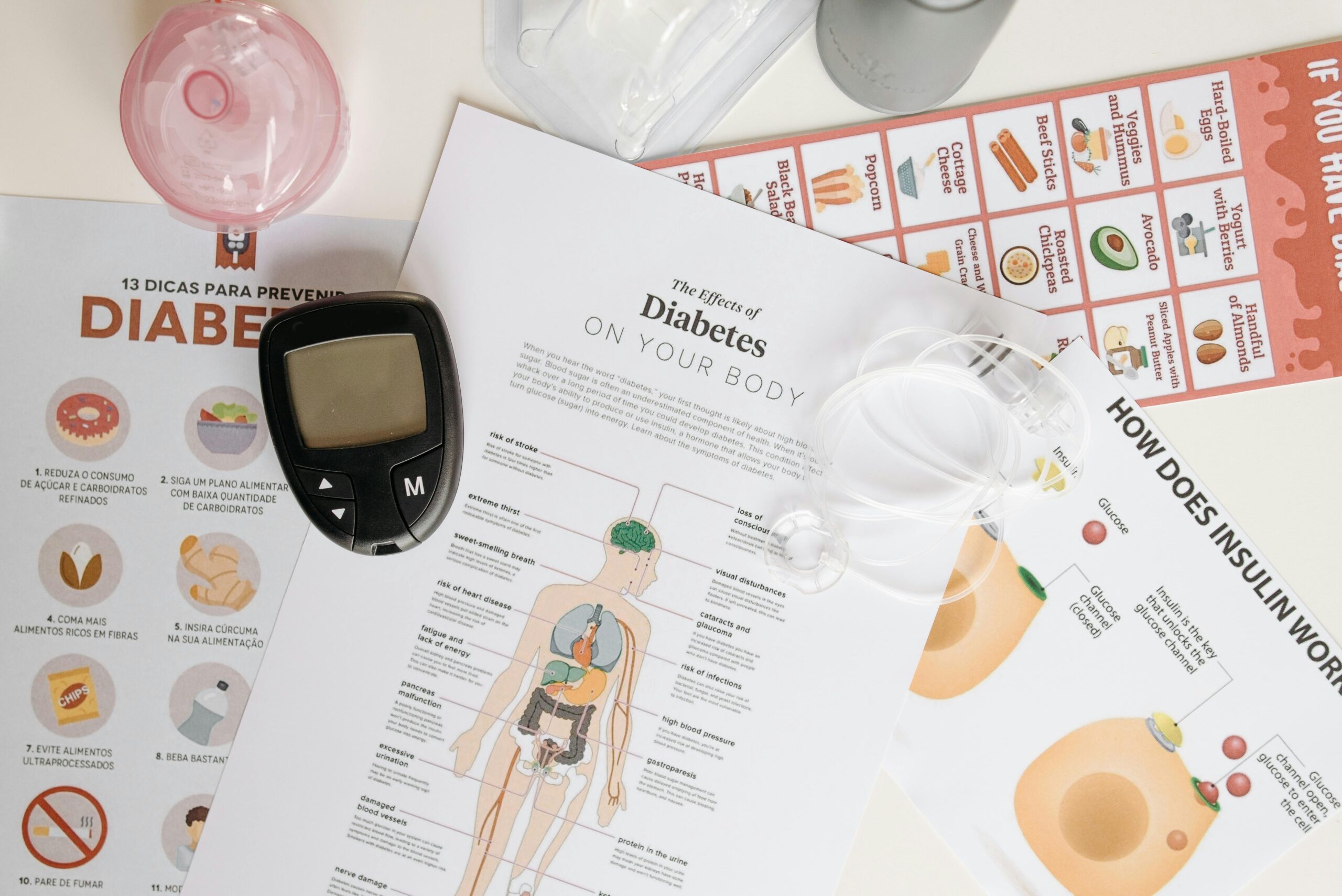
Over time, high blood sugar can be quite harmful.
This is mostly because it harms our neurons and blood vessels and raises the possibility of infection. Persistently elevated blood sugar levels can impair vision and cause peripheral neuropathy,
a condition in which damaged nerves cause loss of feeling in the hands and/or feet. Peripheral vascular disease, heart attacks, and strokes can all be made more likely by damaged blood arteries.